구글과 오라클 간 자바 API의 분쟁 역사 1- (1)
The history of Oracle America, Inc. v. Google, Inc. (1)
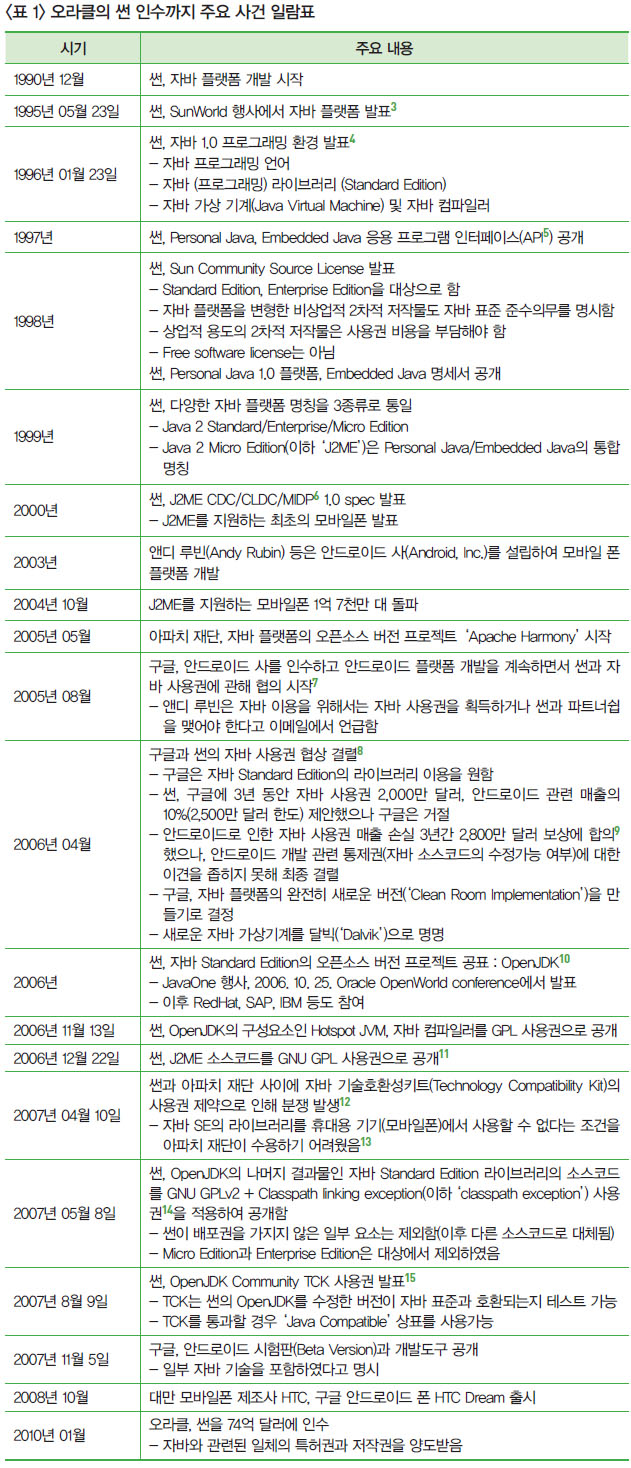
- 1995년 썬(SUN)이 발표한 자바 플랫폼이 SW업계에서 널리 쓰이게 되면서, 썬은 자바 SE(Standard Edition)와 자바 ME(Micro Edition)를 GPL(General Public License)로 공개하였고, 휴대기기용 자바 ME의 사용권 사업에 집중하였음
- 구글은 2005년부터 진행했던 썬과의 자바 사용권 협상이 최종적으로 결렬되자, 2007년 아파치 하모니 프로젝트를 기반으로 개발한 스마트폰용 플랫폼 안드로이드를 아파치 사용권으로 공개하여 널리 보급하였음
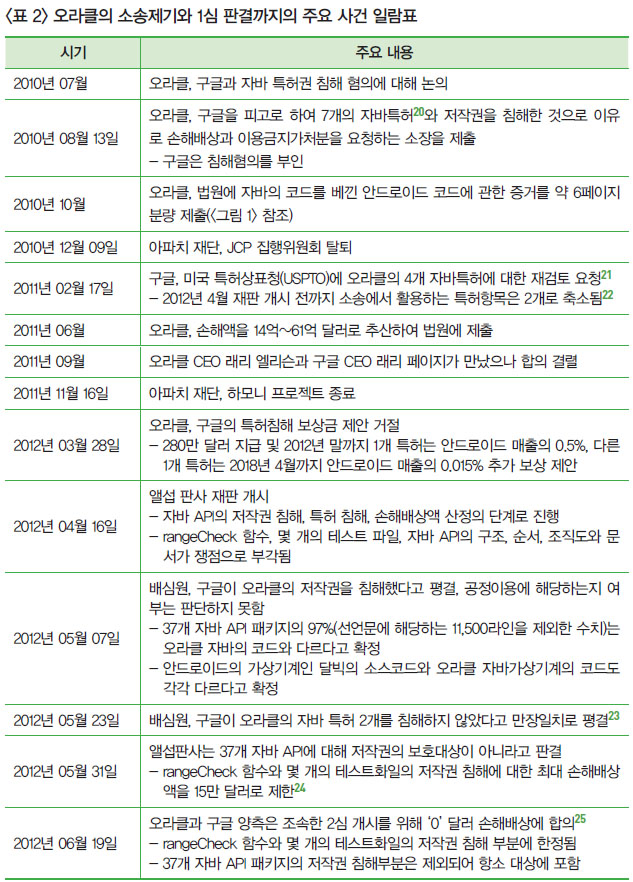
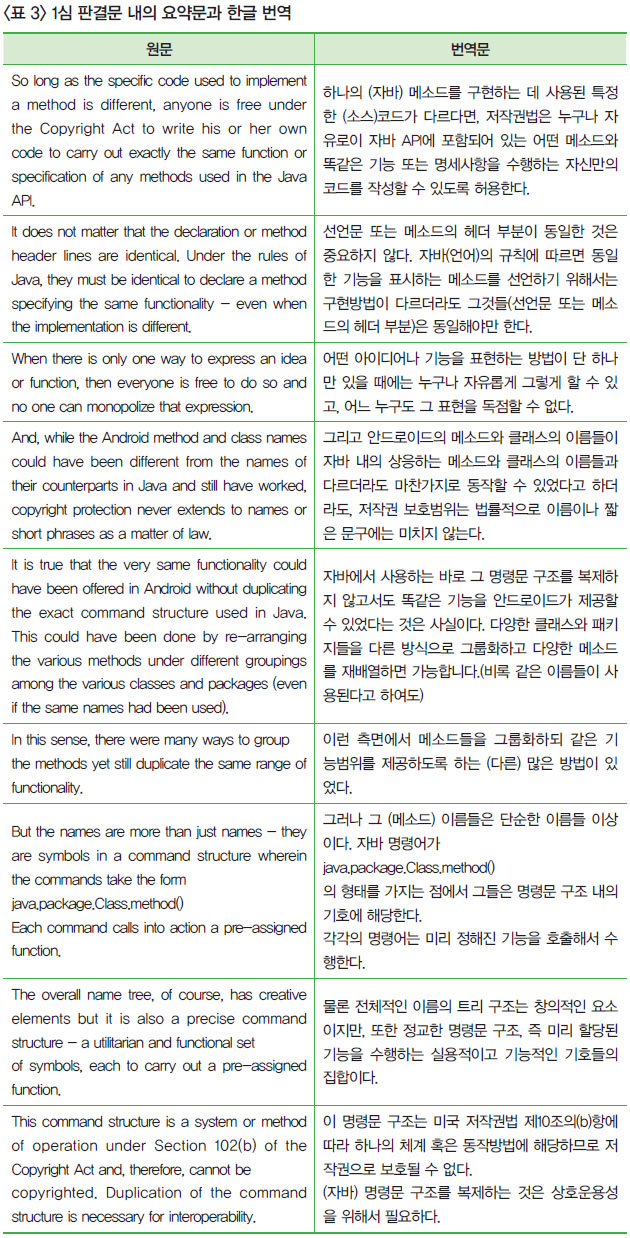
- 2009년에 오라클은 썬을 인수하여 자바 관련 특허권과 저작권을 양도받은 후, 2010년 구글을 상대로 특허권 및 저작권 침해소송을 제기하였는데, 2012년 1심 판결에서 37개 자바 API(Application Programming Interface)의 저작권 침해와 특허권 침해 부분 모두 기각되었음
- 1심 판결에서 배심원은 자바 API의 저작권 침해를 인정했으나 공정이용 여부는 결론을 내리지 못한 데 반해, 1심 판사는 자바 API의 저작권을 인정하지 않았음
- After the Java platform announced by Sun in 1995 became widespread in the SW industry, Sun opened Java SE and Java ME as GPL licenses and focused its licensing business on Java ME for mobile devices.
- After the Java license negotiation between Google and Sun since 2005 was finally broken, Google developed and opened Android based on the Apache Harmony project under the Apache license in 2007.
- In 2009, Oracle got patents and copyrights for Java by acquiring Sun, and in 2010 filed a patent and copyright infringement lawsuit against Google. In the first trial in 2012, the copyright infringement of 37 Java APIs and the patent infringement were all dismissed.
- In the first trial, the jury found that Google had infringed on the copyright related to the Java API, but did not conclude whether it was fair use, whereas the trial judge Alsup determined that the APIs were not copyrightable.
- The government may be able to intervene in terms of increasing consumer welfare, such as capping the fluctuation prices of specific industries in response to the issues from the consumer and firm perspectives.