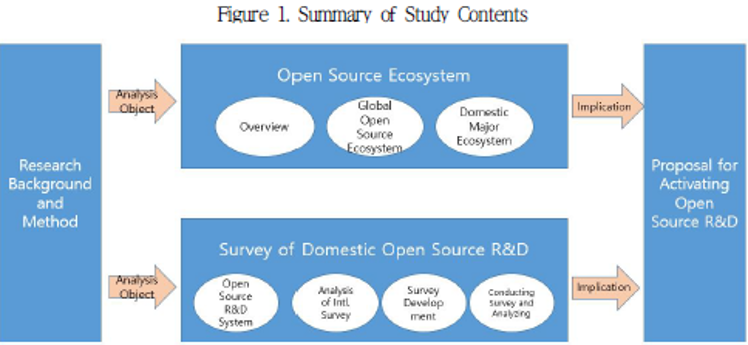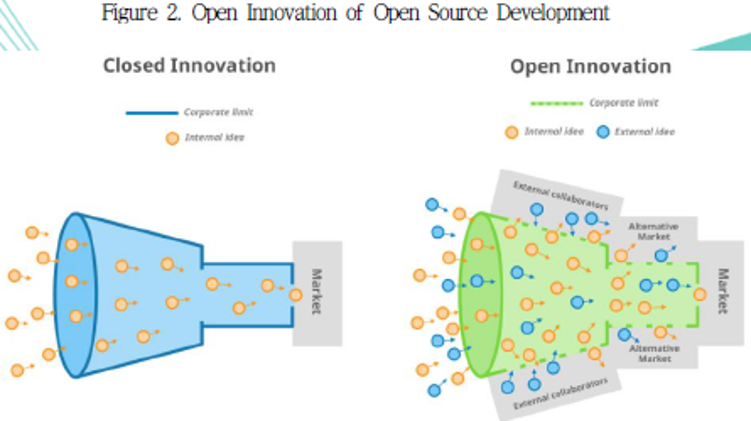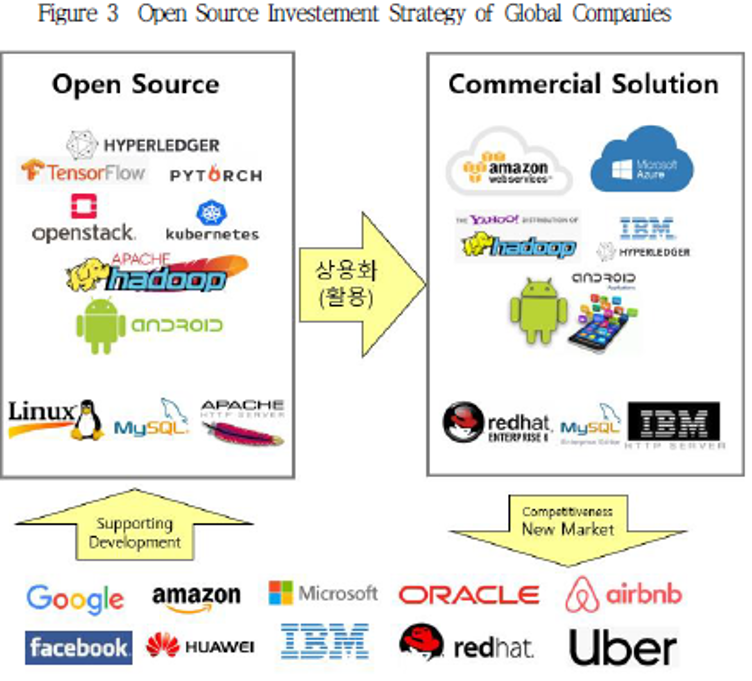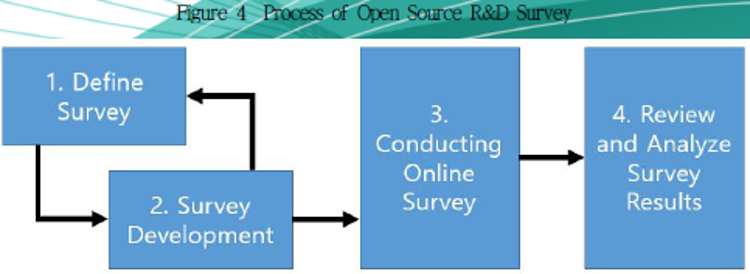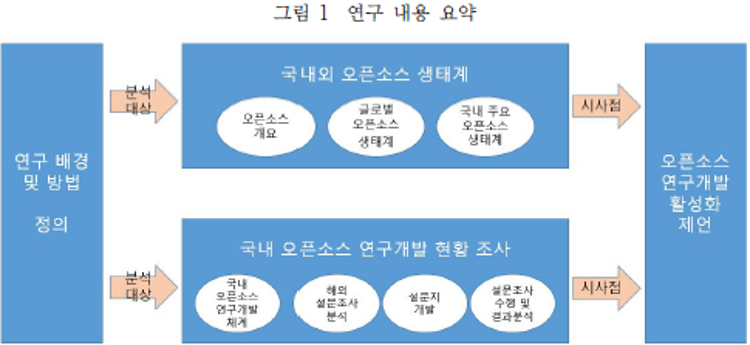
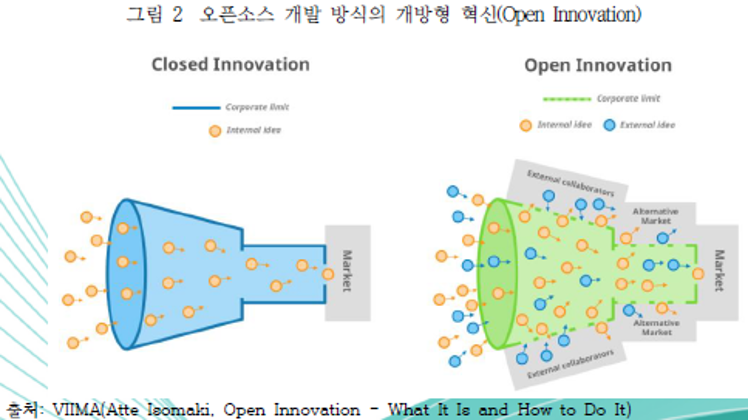
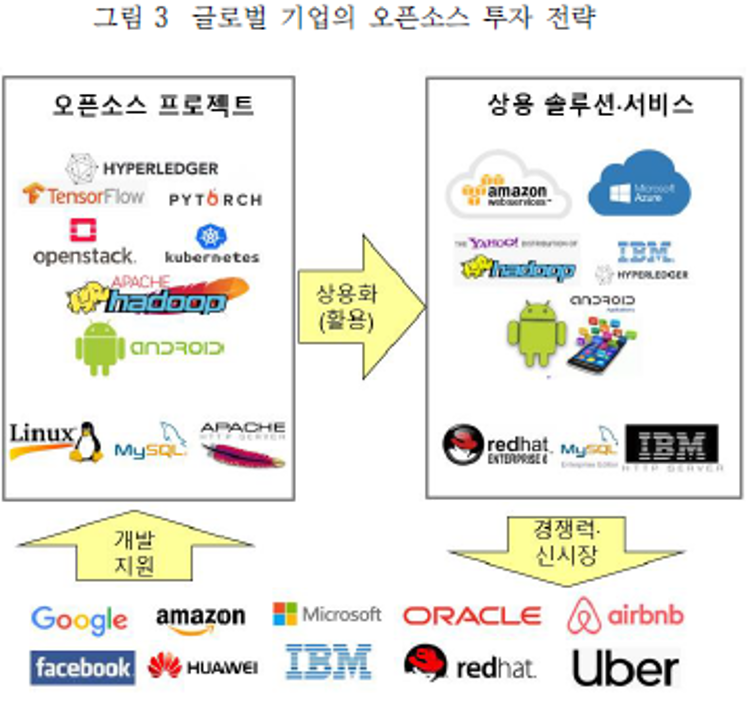
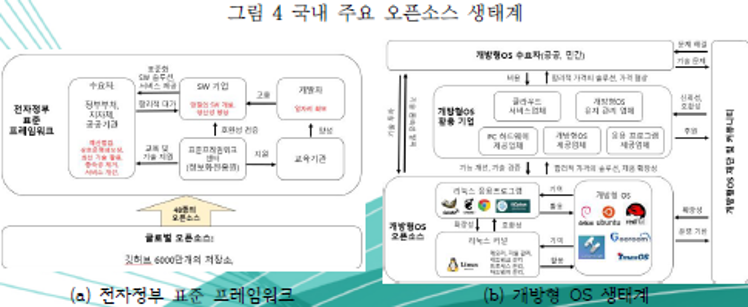

| 분류 | 주요 특징 및 시사점 | |
|---|---|---|
| 오픈소스 | 오픈소스와 라이선스 인식 |
오픈소스 개발 방식의 장점(성과 확산, 외부 협업, 기술 검증)과 오픈소스 사업화(특허권, 보증 부인)에 대한 인식이 기본 인식(오픈소스 활용) 보다 낮음 |
| 오픈소스 성공요인 |
다수의 참여(77.3%)가 가장 많이 응답되었으며 이를 위한 풍부한 문서와 정보 제공과 무료 사용⋅수정 허용 등이 필요 |
|
| 일반적인 오픈소스 활용/개발 |
주요 오픈소스 활용 이유 |
개인적 관심에 의한 오픈소스 활용이 조직의 결정 보다 9% 정도 많았음 오픈소스 활용의 주요 요인은 효율성으로 개인 업무 효율화와 (조직 측면)개발 기간 단축 및 검증 기술 활용임 |
| 주요 오픈소스 활용 분야 |
응용 프로그램, 웹, 운영체제, 데이터베이스 같은 기반 SW 분야 및 응용 프로그램 분야 |
|
| 오픈소스 활용 및 참여 수준 |
정부 연구개발 사업 참여자의 활용 수준이 다소 높으며 보편적 오픈소스 활용 수준은 새로운 모듈/기능 추가임 |
|
| 외부 프로젝트 미참여 이유 |
가장 큰 이유는 시간 부족이며 추가적인 중요 요인은 개인 역량 부족과 회사 정책임 |
|
| 오픈소스 관리 현황 |
조직의 관리 체계 부재가 50%를 넘으며 라이선스 관리 활동 부재도 50%를 넘음 |
|
| 정부 연구개발 결과물 활용 |
결과물 활용 확산을 위해 체계적인 결과물 관리와 홍보가 필요함 |
|
| 정부 연구개발 사업에서 오픈소스 활용 |
오픈소스 활용 이유와 애로사항 |
주요 활용 이유는 효율성이며, 주요 애로사항은 인력 부족과 기술적 어려움 |
| 오픈소스 활용이 중요한 분야 |
SW 신기술(인공지능, 빅데이터, 클라우드) 분야 | |
| 오픈소스 활용 어려움 개선 |
오픈소스 활용의 기술적 어려움 극복을 위한 연구비 확대와 기술 지원이 필요 |
|
| 정부 공개SW 연구개발 |
과제 참여 | 주 참여 이유는 공개SW 개발 경험 획득과 최신 기술 선도를 위한 R&D 사업 참여였으며 주 미참여 이유는 공개SW 개발 역량 부족과 공개SW 과제 정보 부족임 |
| 현황 | 과제 참여시 주요 애로사항 |
숙련된 공개SW 개발자 부족과 다양한 오픈소스 개발의 기술적 어려움(커뮤니티 관리, 연구개발 전략 부족, 기술 지원 부재 등) |
| 과제 중요성 | 공개SW 생태계 중요성, 공개SW 역량 강화, 공개SW 인재 양성, 유망 공개SW 발굴 및 최신 기술 개발 |
|
| 사업 확신이 필요한 분야 |
SW 신기술(인공지능, 빅데이터, 클라우드) 분야 | |
| 기획⋅선정 단계 주요 개선사항 |
오픈소스 연구개발 어려움을 고려한 연구 예산 증액과 체계적인 기획 및 평가를 위한 오픈소스 현황 조사 |
|
| 수행 단계 주요 개선사항 |
오픈소스 연구개발 활성화를 위한 인센티브 강화와 커뮤니티 활성화 지원, 라이선스 및 보안 취약점 검증 지원 등의 오픈소스 연구개발 지원 |
|
| 사후 관리 주요 개선 사항 |
결과물 활용 확산을 위한 체계적인 결과물 관리와 사후 연구 및 관리 체계 필요함 |
|